Useful Informations
Resistance Guided Therapy (RGT)

The misuse and overuse of antibiotics has impacted their effectiveness globally. Diagnostics that detect infection and genetic markers for antibiotic resistance in a single test enable you to implement Resistance Guided Therapy (RGT). Utilising an RGT approach is clinically demonstrated to improve patient cure rates1 and is recommended by international bodies as the preferred method of treatment for infections such as Mycoplasma genitalium (Mgen) or gonorrhoea.2-6
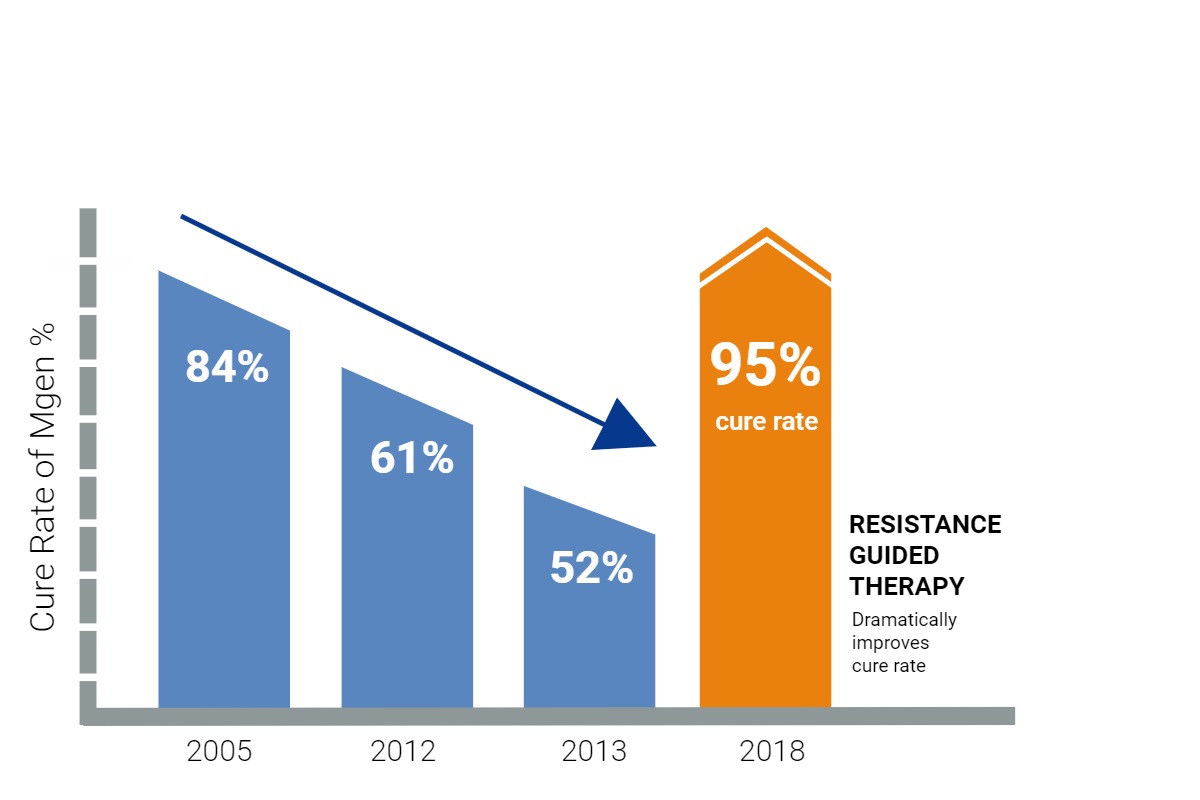
Declining cure rates when employing detection-only practices for M. genitalium addressed with implementation of RGT, increasing cure rates for macrolide susceptible populations to 95% and total population cure rate over 92%.1
What is Resistance Guided (RGT) Therapy?
Resistance Guided Therapy (RGT) uses advances in diagnostic technology to help clinicians choose the best targeted therapy for individual patients based on the resistance status of their infection.
- • RGT uses tests that detect the infecting organism and genetic markers linked to antibiotic susceptibility or infection
- • RGT can replace empiric treatment models by providing additional information at the time of diagnosis to guide appropriate treatment decisions
Why is Resistance Guided Therapy important?
Strategies for controlling many STIs are dependent on the availability of inexpensive yet highly effective antibiotics. As antimicrobial resistance rates rise in these infections it is even more important to use our limited antibiotics more wisely.
Guidelines for management of STIs caused by Mycoplasma genitalium and Neisseria gonorrhoeae increasingly recommend RGT to help:
- • improve likelihood of effective patient treatment
- • reduce re-admission and healthcare costs
- • minimise the spread of antibiotic resistant infections
- • maintain the efficacy of antibiotic treatment (antibiotic stewardship)
SpeeDx ResistancePlus® diagnostics detect the infecting organism and antibiotic susceptibility or resistance markers – empowering clinicians to make informed patient treatment decisions.